Elastic Sheet Swimming using Dynamic Magnetic Fields
Scientific Achievement
Swimming of homogeneous 2D elastic sheets made from magnetic particles.
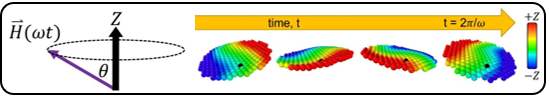
Upper, left: Magnetic field H ⃑ rotating around an axis.
Upper, right: Transverse waves propagating around the sheet with negligible sheet rotation (see black particle).
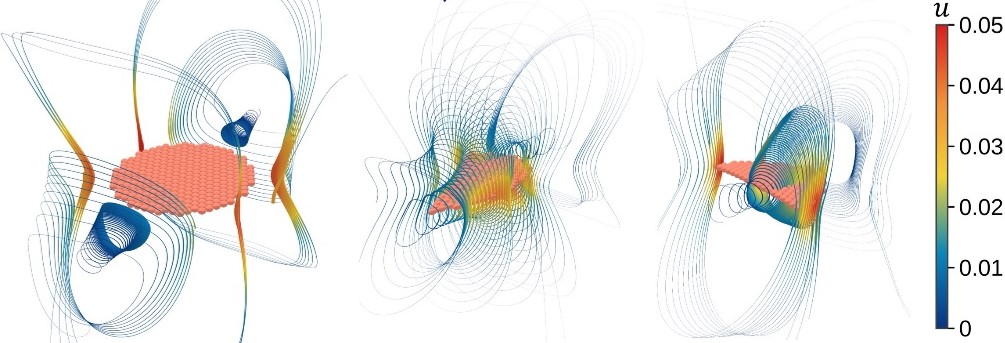
Middle: Uncut (left) and cut (center, right) magnetic sheet causing fluid flow around the sheet, u.
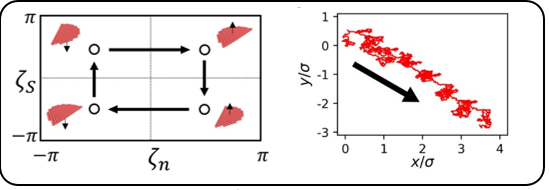
Lower, left: Swimming is induced by manipulating the sheet to control the orientation of the cut (ζS) and face (ζn).
Lower, right: Lateral motion of sheet over time.
Significance and Impact
Understanding how to use a dynamic magnetic field and sheet symmetry to induce locomotion reduces the complexity of sheet synthesis and advances the design of autonomous, soft microrobots.
Research Details
-
Above a critical rotation frequency for the magnetic field, traveling waves are produced around the magnetic sheet.
-
Fluid flow caused by the motion of a sheet with broken symmetry moves the sheet along a circular path.
-
A sequence of nonreciprocal sheet motion will cause swimming along a predetermined path.
-
The swimming velocity can be computed by accounting for the broken sheet symmetry.
Locomotion of magnetoelastic membranes in viscous fluids
Brisbois, CA; Olvera de la Cruz, M
Physical Review Research, 4, 2022, 023166.
Work performed at Northwestern University