Record Photoreduction of CO2 in Water Sensitized by Quantum Dots
Scientific Achievement
CuInS2 quantum dots (QDs) photosensitize a Co-porphyrin catalyst to reduce CO2 to CO in pure water at pH 6-7 with turnover number (TONCO) >80,000, quantum yield (QYCO) >5.2%, and selectivity (SCO) >99%.
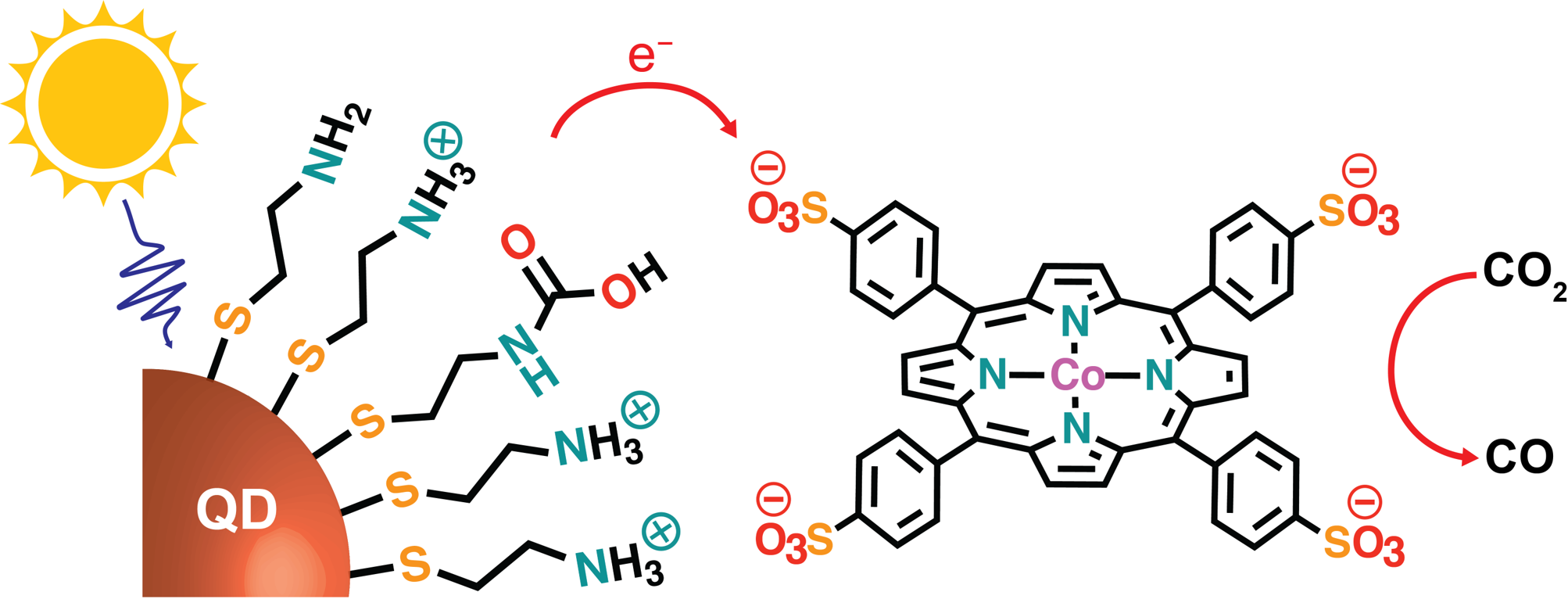
Quantum dots/porphyrin system effectively converts CO2 with respect to all three key metrics (TONCO, QYCO and SCO). The performance of the QD system greatly exceeds that of the benchmark [Ru(bpy)3]2+-CoTPPS aqueous system due primarily to electrostatic attraction of the QD to the catalyst, which promotes fast multielectron delivery, and termination of the QD’s ligand shell with free amines, which pre-activate CO2 as carbamic acid.
Significance and Impact
The breakthrough efficiency achieved in this work represents a major step in the realization of reaction networks and soft matter for direct solar-to-fuel conversion with a TONCO that is a factor of 90 greater than the best aqueous system, which uses [Ru(bpy)3]2+ as sensitizer.
Research Details
-
The exceptional performance comes from the amine-terminated ligand shells of the QDs, which promote electrostatic assembly of sensitizers and catalysts and provide basic surface sites for CO2 adsorption and activation.
-
The QD-driven system operates in pure unbuffered water, whereas the current highest performing molecule-sensitized systems only operate in solutions buffered at high pH, thus limiting their potential for larger scale CO production.
-
This photocatalytic system should be well suited for direct capture of CO2 from air.
Quantum Dot-sensitized Photoreduction of CO2 in Water with Turnover Number >80,000
Arcudi, F.; Ðorđević, L.; Nagasing, B.; Stupp, S.; Weiss, E. A
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 143, 43, 18131, 2021
Work Performed at Northwestern University.
