Using Magnetic Fields to Control Elastic Sheets
December 20, 2019
Scientific Achievement
Rotating magnetic fields can drive 2D elastic sheets, made of magnetic particles, to expand, contract, or twist.
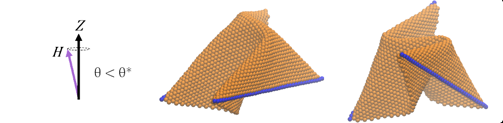
Sheets in a tight-rotating magnetic field.
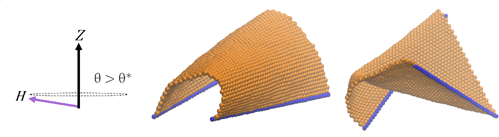
Sheets in a wide-rotating magnetic field.
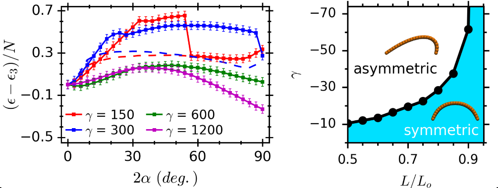
Left: Dependence of a sheet’s total energy on the twisting angle of its boundaries (2α) in a tight-rotating field.
Right: Sheet symmetry dependence on field strength (|γ|) and boundary separation (L/L_o) in a wide-rotating magnetic fields.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the effects of dynamic magnetic fields on the shape and symmetry of elastic sheets advances the design of autonomous, soft microrobots.
Research Details
- Forces on sheet boundaries can be manipulated by changing the angle of rotating magnetic fields above and below a critical value, θ^∗.
- Changing magnetic field strength,|γ|, in fields rotating below a critical angle can enhance or resist torque on sheet boundaries.
- Rotating magnetic fields above a critical angle can induce spontaneous symmetry breaking
Actuation of Magnetoelastic Membranes in Precessing Magnetic Fields
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116, 2500-2505
Work Performed at Northwestern University
